Computer vision (CV) is a field of artificial intelligence (AI) that uses machine learning and neural networks to enable computers and systems to understand and interpret the visual world. It replicates the complexity of human vision. And thanks to advances in AI, the field has been able to not only match, but also surpass humans in some CV tasks related to image recognition and object detection and labeling.
A Growing Market
In 2020, the value of the AI image recognition market was $1.7 billion and it is expected to reach $5.2 billion by 2026. Its growth is driven by software and hardware innovations but primarily by the amount of data being generated today. More data means more visual input to train and make CV better.
How It Works
Deep learning, a type of machine learning, and a convolutional neural network (CNN) are the two technologies used to accomplish computer vision tasks.
- Machine learning uses algorithmic models that enable a machine to continuously learn and teach itself to process visual data.
- CNN breaks down visual data into pixels and gives them tags or labels. This process helps the machine learning or deep learning model to “see.” The CNN then runs predictions and checks for accuracy until the model can understand images.
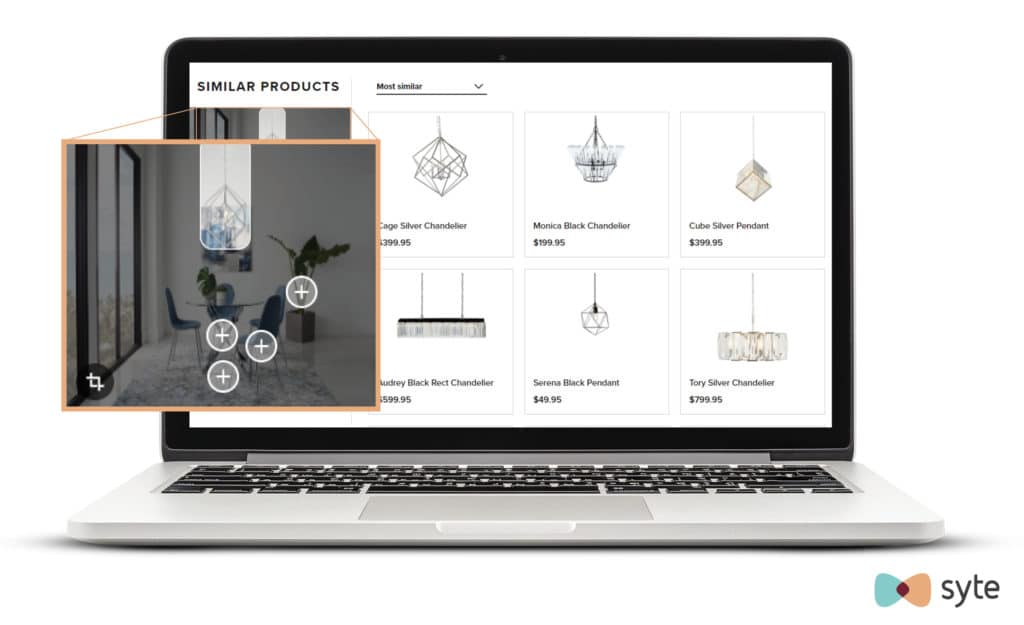 City Furniture’s visual search feature is an example of a computer vision application.
City Furniture’s visual search feature is an example of a computer vision application.
Computer Vision Use Cases in Retail and eCommerce
Computer vision is being used widely across different industries. Autonomous driving, security cameras, medical imaging analysis, and cashierless stores are some of its applications. In retail and eCommerce, CV provides a lot of potential for improving business operations and customer experiences. Here are some sample use cases for brick-and-mortar and eCommerce retailers:
- Inventory visibility and management – Through robotics, computer vision can take over the monotonous task of ensuring that inventory is accurate and updated. Shelf-scanning robots can capture real-time product insights for stock replenishment, demand planning, and product compliance.
- Shopper data – Computer vision can identify customers and recognize behaviors. This provides retailers with multiple opportunities to improve the in-store experience by customizing store and product layouts, and optimizing prices and promotions.
- Visual search – In eCommerce, computer vision allows shoppers to search a brand’s website and inventory using an image, instead of text. Camera search removes the friction of having to think of the right keyword to search for, offering a faster and easier site search experience.
- Product recommendations – Supporting visual product discovery, computer vision can surface visually similar or related items to products that shoppers are already viewing. Because the recommended items can be based on current browsing behavior and previous purchases, brands are better able to personalize the experience of customers.
- Deep product tagging – CV automatically extracts information from product image data and assigns relevant tags. The process is more accurate and less prone to errors than manually tagging products. Well-organized product tags are the foundation of effective online merchandising, search filtering, navigation, and search results.
- Augmented reality – Combining real-world scenarios with computer-generated elements, augmented reality provides interactive online shopping experiences that help to contextualize products, allow shoppers to virtually try on items, and more.