Visual artificial intelligence, or simply, visual AI, is a discipline of computer science that enables machines to identify, understand, and act on imagery and visual data just like a human vision system. It combines several technologies, including computer vision, natural language processing (NLP), different content formats (video, photos, and extended reality), and deep learning to derive insights and create business value from images.

How Visual AI Works
Computer vision is the main AI subfield that provides computers the capability to see and learn how to recognize objects and human faces on visual data. Different types of computer vision tasks may include looking for text, images, or faces. But it doesn’t end there. What allows a machine to actually detect, understand, and categorize specific objects within a visual input is image recognition.
To do visual AI at scale, it utilizes neural networks, large computing power, algorithms, and training techniques to learn complex data patterns processed in image recognition. This is made possible by another AI subfield called deep learning. Depending on the use case, NLP is also utilized to perform and complete visual AI tasks.
What are Examples of Visual AI Use Cases?
Visual AI can be applied to a variety of use cases, including:
- Document classification which enables access to information by combining computer vision and NLP to classify, extract, and enrich documents.
- Product detection and search which identifies products within images and searches a given catalog for exact matches.
- Visual search which is a search engine that looks for information through the input of an image and/or displays visual search results.
How Organizations Across Industries Use It
Every industry has a high demand for visual AI capabilities such as systems that can be used for automation to boost productivity, personalization to improve the customer experience, research to fasten learning and innovation, and more.
In healthcare, providers use the technology, specifically imaging technologies, to automate the examination, detection, and diagnosis of health issues from devices such as X-rays and CT scans. Insurance companies can assess vehicle damage more accurately, reducing fraud and resource waste during the claims process.
In manufacturing, visual AI can be used to detect product defects, predict maintenance, and more. Retail brands, on the other hand, can apply it in various applications that both make the online shopping experience engaging and valuable for customers, and enhance backend operations.
Visual AI Benefits for Retailers and eCommerce Brands
Retail is one of the most dynamic industries that can gain huge benefits from visual AI. With the rapid growth of eCommerce and consumers being more comfortable shopping both online and offline, it is becoming a key differentiator and critical capability that can separate leading brands from the rest. Some of its benefits include:
- Seamless product discovery with the use, for example, of a visual search engine that delivers accurate and relevant search results, and a Pinterest-like tool that allows shoppers to view similar items to an image of interest.
- Better customer experience with relationship-building recommendation engines that suggest products like a family or friend, based on visual data and real-time context. Applications include “Complete the Look,” “Similar Products,” and “Customers Also Bought.”
- More efficient backend processes using insights generated from search query data and user interactions with on-site image assets that inform business decisions, inventory management, and trend and demand forecasts.
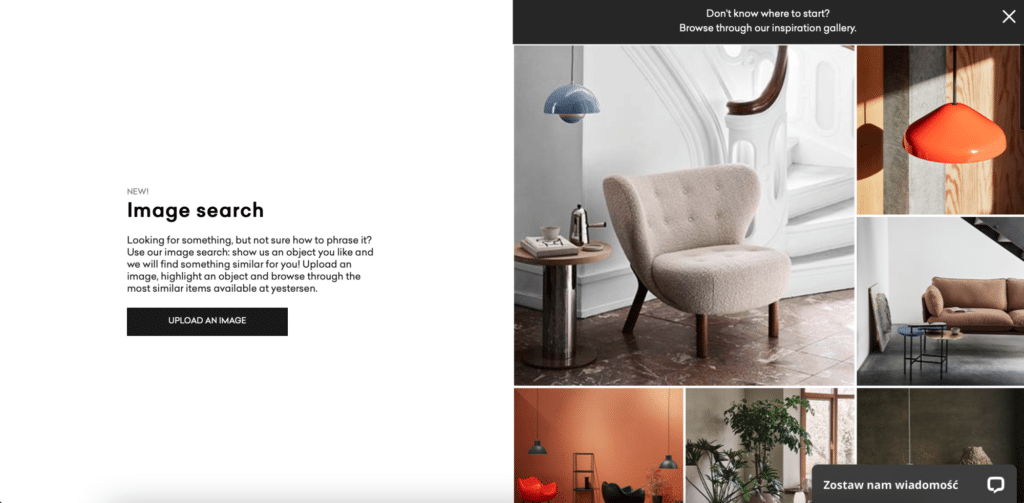 yestersen implements a visual AI solution on the website with image search
yestersen implements a visual AI solution on the website with image search